Artificial Intelligence explained: from origins to agentic systems
AI & Modern Engineering Practices
In today's article: what is Artificial Intelligence (AI), how it works, its risks, careers, and its role in modern engineering.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence is no longer a futuristic concept confined to research labs or science fiction. Today, AI systems are embedded in modern software, cloud platforms, and decision-making processes, shaping how organizations operate at scale. From recommendation engines and fraud detection to AI-assisted development and autonomous systems, artificial intelligence has quietly become infrastructure.
Yet, despite its ubiquity, Artificial Intelligence remains widely misunderstood. Many teams rely on AI-driven tools daily without being able to clearly explain what AI is, how it works, or why some AI initiatives succeed while others fail. This lack of clarity fuels inflated expectations, poorly scoped projects, and systems that look impressive in demos but collapse in production.
This article exists to change that. Rather than repeating hype or simplifying AI into slogans, this guide explains Artificial Intelligence as it is actually used today: its origins, technical foundations, core architectures, different forms, operational risks, and its growing dependence on cloud computing and DevOps practices. If AI is becoming foundational to modern engineering, then understanding it clearly is no longer optional.
Let’s start at the beginning.
What is Artificial Intelligence in one sentence (and what is it not)?
Artificial Intelligence is the field of building systems that learn from data, recognize patterns, and support or automate decisions without being explicitly programmed step by step.
What Artificial Intelligence is not
AI is often misunderstood by association. To be clear:
It is not a single technology.
It is not equivalent to ChatGPT or generative models.
It is not autonomous intelligence that “thinks” like humans.
Artificial intelligence systems do not possess intent, consciousness, or understanding. They operate by optimizing statistical representations of reality based on data, models, and constraints defined by humans.
When an AI system appears “smart,” it is usually because it has access to high-quality data, sufficient computing power, and a well-designed operational context. Understanding this distinction early prevents most strategic and architectural mistakes.
When did Artificial Intelligence originate, and why does it evolve in waves?
Artificial Intelligence did not emerge suddenly. The history of AI is defined by cycles of optimism, limitation, and resurgence, driven by advances in mathematics, computing power, and data availability.
The conceptual foundations of AI date back to the mid-20th century, when researchers like Alan Turing questioned whether machines could simulate human reasoning. Early symbolic AI systems attempted to encode logic and rules explicitly, but they struggled with real-world ambiguity and scale.
The first major wave of AI optimism peaked in the 1950s and 1960s, followed by the first “AI winter,” when limited hardware and unrealistic expectations slowed progress. Similar cycles repeated in the 1980s and 1990s as expert systems and early neural networks failed to scale reliably.
Why modern AI is different from earlier waves
The modern resurgence of Artificial Intelligence is different for one fundamental reason: infrastructure. Cloud computing, distributed storage, specialized hardware such as GPUs and TPUs, and massive datasets transformed AI from a theoretical discipline into an applied engineering field.
Deep learning became viable not because the algorithms were new, but because the environment finally supported them. This infrastructure-driven acceleration explains why AI adoption feels sudden, even though the ideas behind it are decades old and why many organizations still struggle to move from experimentation to production.
What is the difference between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
One of the most persistent sources of confusion in artificial intelligence is the relationship between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning.
Artificial Intelligence is the umbrella term. It includes any system designed to simulate intelligent behavior.
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI focused on systems that learn patterns from data rather than following hard-coded rules.
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that uses multi-layer neural networks to model complex, non-linear relationships.
Not all AI systems use machine learning, and not all machine learning relies on deep learning. In production environments, many AI applications still depend on simpler statistical or rule-based models because they are easier to interpret, cheaper to operate, and more predictable.
The strategic mistake is assuming that more complex AI models automatically deliver more value. In reality, value emerges when model complexity aligns with business context and operational constraints.
How does Artificial Intelligence work at a high level?
At its core, every Artificial Intelligence system relies on three pillars: data, models, and compute.
Data provides the raw material.
Models define how patterns are learned.
Compute provides the processing power to train and run AI systems at scale.
The AI system lifecycle in practice
Most AI systems follow a lifecycle that includes:
Data collection, cleaning, and structuring
Model training to detect patterns or relationships
Evaluation, deployment, and monitoring
Continuous feedback loops to adapt over time
What differentiates reliable AI systems from fragile ones is not algorithmic sophistication, but the quality of the operational pipeline around them. This is where cloud-native architectures and DevOps practices become decisive.
What types of AI systems are used in practice today?
Traditional and predictive AI
Traditional AI systems focus on classification, forecasting, and optimization. They power credit scoring, demand forecasting, anomaly detection, and many enterprise workflows. These AI models excel at consistency and precision within defined boundaries.
Generative AI
Generative AI systems create new content such as text, images, audio, or code by learning probabilistic representations of existing data. While powerful, generative AI introduces new risks related to hallucination, bias, and governance that must be actively managed.
Agentic AI and AI agents
Agentic AI systems go beyond single-task execution. They combine reasoning, memory, and action, allowing AI agents to plan steps, interact with tools, and adapt based on outcomes. This shift from AI as a tool to AI as an agent fundamentally changes how artificial intelligence integrates with engineering workflows.
Agentic systems such as ACE Dev, an Agentic AI Cloud Engineer, apply this paradigm directly to cloud and DevOps operations, automating decisions with contextual awareness rather than static scripts.
What careers and professional paths exist in Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence is not a single career path. In practice, AI spans multiple disciplines that intersect with data, infrastructure, product, and governance.
Core AI roles
Machine Learning Engineer.
Data Scientist.
Applied AI / LLM Engineer.
Research Scientist.
Adjacent and critical roles
Data Engineer and Analytics Engineer.
MLOps / LLMOps Engineer.
Platform and Cloud Engineer for AI workloads.
AI Product Manager.
AI Security and Governance Specialist.
Many organizations fail by hiring model specialists without investing in these adjacent roles. Reliable AI systems emerge from teams, not isolated expertise.
Why do so many AI projects fail in production?
Most AI initiatives fail for reasons that are organizational, not mathematical, such as:
Poorly defined success metrics.
Lack of production-grade infrastructure.
Absence of monitoring and feedback loops.
Misalignment between data science and engineering teams.
Artificial Intelligence does not eliminate complexity; it redistributes it. Without DevOps and operational discipline, complexity accumulates silently until systems break.
Why cloud and DevOps are prerequisites for AI in engineering
AI workloads are inherently elastic, data-intensive, and failure-prone. This makes cloud infrastructure essential, not optional.
DevOps practices enable:
Continuous delivery for AI models.
Observability for predictions and drift.
Cost governance for compute-intensive AI workloads.
Organizations that treat AI as “just another feature” consistently underestimate its operational footprint.
What are real-world use cases of Artificial Intelligence?
AI creates value when tied to outcomes, not capabilities:
Decision support and prioritization.
Operational automation.
Reliability and risk reduction.
Cognitive load reduction for engineering teams.
This shift from efficiency to strategic leverage is where mature organizations differentiate themselves.
AI in practice, not theory. Explore real-world AI implementations across cloud, DevOps, and operations.
What risks and ethical challenges does AI introduce?
Artificial Intelligence introduces systemic risks, including:
Bias amplification.
Data leakage.
Over-automation.
Loss of accountability.
Responsible AI requires governance embedded into pipelines, not retrofitted after incidents.
What is the difference between weak AI and strong AI?
Most AI systems today are examples of weak AI: narrow, task-specific intelligence. Strong AI, capable of generalized reasoning across domains, remains theoretical.
Understanding this distinction prevents unrealistic expectations and helps leaders invest in what is achievable now.
Where is Artificial Intelligence heading next?
The future of Artificial Intelligence is not defined by smarter models alone, but by smarter systems:
Context-aware automation.
Agentic infrastructure.
Human-AI collaboration.
This evolution depends on operational maturity as much as algorithmic progress.
Frequently asked questions about AI
What is Artificial Intelligence in simple terms?
AI refers to systems that learn from data to support or automate decisions.
Is AI the same as machine learning?
No. Machine learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence.
Is generative AI replacing traditional AI?
No. Both coexist and serve different purposes.
Can AI work without cloud infrastructure?
In limited cases, yes. At scale, cloud becomes essential.
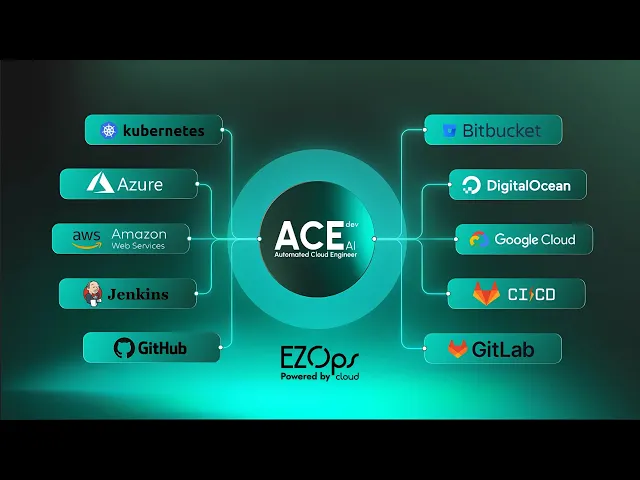
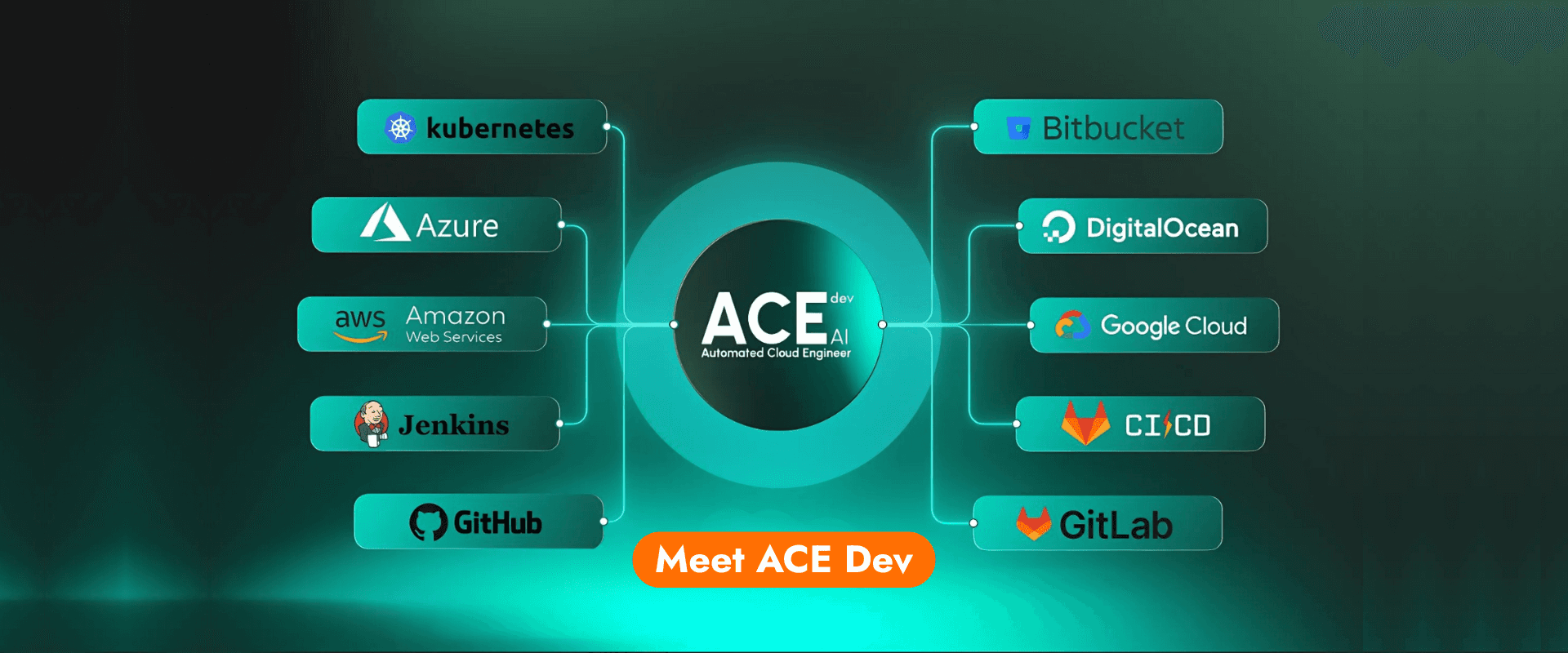
What is ACE Dev and what does it do?
ACE Dev is an Agentic AI Cloud Engineer designed to operate agentically across cloud and DevOps workflows. Instead of executing static scripts, it applies contextual reasoning to automate decisions related to infrastructure, reliability, and operations, acting as a continuous engineering layer rather than a single tool. Learn more at https://acedev.ai/.
Conclusion: AI as capability, not hype
Artificial Intelligence is not magic. It is a capability that emerges when data, infrastructure, and operational discipline align. Organizations that treat AI as strategy, rather than spectacle, will define the next decade of engineering.
The rest will keep chasing demos.


EZOps Cloud delivers secure and efficient Cloud and DevOps solutions worldwide, backed by a proven track record and a team of real experts dedicated to your growth, making us a top choice in the field.
EZOps Cloud: Cloud and DevOps merging expertise and innovation



